Why Canadian public healthcare fails Lyme patients and why they seek treatment elsewhere
Promoting Canadian research and researchers.
Insert HTML here

Promoting Canadian research and researchers.

This in-depth article by Cox and Levesque gives context to many of the systemic barriers that Canadian Lyme patients encounter, and highlights the important role that patient organizations play in addressing those barriers.
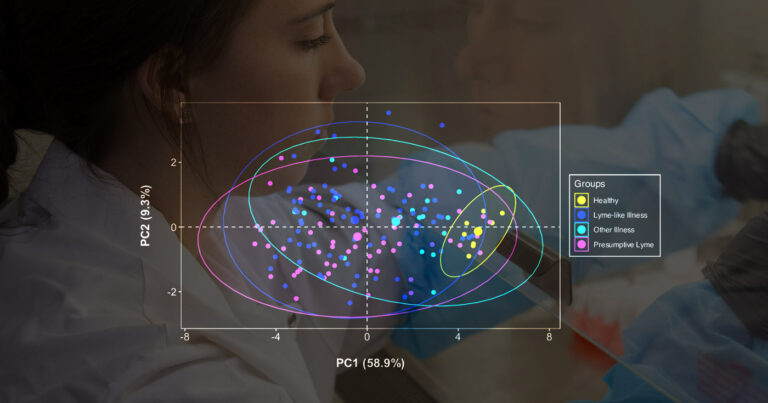
Examining serology and the health burden of Lyme disease and chronic illness with Victoria Sanderson at the G Magnotta Lab.

Background Lyme borreliosis (LB), caused by Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb), is the most common tick-borne infection in Germany. Antibodies against Bb are prevalent in the general population but information on temporal changes of prevalence and estimates of seroconversion (seroincidence) and seroreversion are lacking, especially for children and adolescents. Aim We aimed at assessing antibodies against Bb and factors associated with seropositivity…

Recent calls to action by Dr. Monica Embers and Dr. John Aucott.
Abstract The tick, Ixodes scapularis, vectors pathogens such as Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium that causes Lyme disease. Over the last few decades I. scapularis has expanded its range, introducing a novel health threat into these areas. Warming temperatures appear to be one cause of its range expansion to the north. However, other factors are also involved. We show that…
Abstract This study aimed to demonstrate that severe neurological motor deficits in the context of late tick-borne disease with mixed microorganism involvement are eligible for long-term combined antibiotic/antiparasitic treatments. The inclusion criteria were: 1. neurological limb paralysis with a disability score >4 according to the EDSS Kurtzke disability scale; 2. serological tests pointing to an…
Abstract This study aimed to demonstrate that severe neurological motor deficits in the context of late tick-borne disease with mixed microorganism involvement are eligible for long-term combined antibiotic/antiparasitic treatments. The inclusion criteria were: 1. neurological limb paralysis with a disability score >4 according to the EDSS Kurtzke disability scale; 2. serological tests pointing to an…
Published November 2022 Background: Lyme disease (LD) is a complex tick-borne pathology caused by Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato bacteria. Currently, there are limited data regarding the health outcomes of people infected during pregnancy, the potential for perinatal transmission to their fetus, and the long-term effects on these children. Therefore, the primary objective of this survey study was to…
An article by Usha Lee McFarling October 10, 2022 “A doctor’s humbling journey treating long Covid: ‘The second we think we know what we are doing, we fall flat on our face’” “Unfortunately way too many people with this are not being believed about their illness. And this has happened before, with long Lyme, and…
“The following is a list of peer-reviewed articles that support the evidence of Lyme and other tick-borne diseases causing neuropsychiatric illness. It is organized into two different categories— neuropsychiatric symptoms and dementia” source unknown. Access list of citations
Abstract Background: Erythema migrans (EM) is the hallmark manifestation of the Lyme borreliosis (LB), and therefore its presence and recognition are sufficient to make a diagnosis and to start proper antibiotic treatment to attempt to eradicate the infection. Methods: In this study we compared the clinical data of 439 patients who presented an EM either…
Abstract Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis (HGA) is an infection caused by the intracellular bacterium Anaplasma phagocytophilum. As a tick-borne disease, the public health impact of HGA continues to increase with range expansion of the disease vector. The clinical presentation of HGA is often a non-specific febrile illness. The presence of leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and mild hepatic injury are frequently noted…
Abstract Lyme disease (LD), caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, is the most common vector-borne disease in USA and Europe. Despite the standard 2-4 weeks antibiotic treatment, approximately 10%-20% of patients will develop post-treatment LD syndrome, a condition that is poorly understood. One of the probable causes is thought to be the presence of B. burgdorferi persister forms that are not…
July 26, 2022 Abstract Lyme disease (LD), caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, is the most common vector-borne disease in USA and Europe. Despite the standard 2-4 weeks antibiotic treatment, approximately 10%-20% of patients will develop post-treatment LD syndrome, a condition that is poorly understood. One of the probable causes is thought to be the presence of B. burgdorferi persister forms…